

This method involves sterilizing waste by exposing it to a cobalt source. The shredding process results in a volume reduction, and energy use is reportedly lower than that of an incinerator. As with autoclaving, approximately 90% of medical wastes can be treated with this process. Computerized controls are employed to ensure the minimum parameters for disinfection and proper equipment function. Waste is first shredded, and then mixed with water and internally heated to neutralize all present biologicals.

The application of microwave technology treatment also can disinfect waste. The resulting liquids are placed into the sewer system, while solid residues are disposed in landfills. Grinding ensures sufficient exposure of the chemical agent to all parts of the waste and assists in easy disposal of any residues.

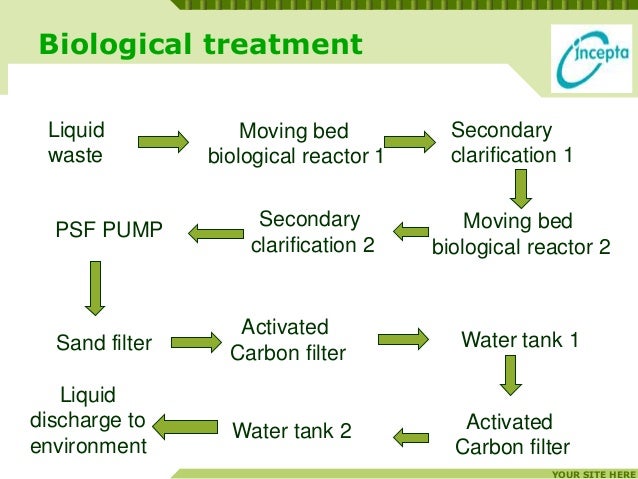
There are a number of factors that should be considered regarding the effective usage, including: the types and biology of microorganisms in the wastes, degree of contamination, type of disinfectant used as well as its concentration and quantity, contact time, and mixing requirements.Īnother option is the grinding of medical waste before exposing it to a liquid chemical disinfectant. Chemical disinfection processes are most appropriate for liquid wastes, although they can still be used to treat solid wastes. This process involves the use of chemical agents for disinfection, such as chlorine, for liquid waste disinfection. It’s important to note that the EPA does not recommend ethylene oxide for treating infectious wastes because of its toxicity. The gas that comes into contact with the waste will kill harmful, infectious agents. In this process, medical waste is fed into an evacuated air-tight chamber and treated with gas sterilization agents (such as ethylene oxide or formaldehyde). Autoclaves are not suitable, however, for pathological, cytotoxic, or other toxic chemical wastes. This assures the destruction of microorganisms.Īpproximately 90% of regulated medical wastes, including microbiological waste disposal, are suitable for autoclaving. Bags of waste are placed in a chamber and steam is introduced for a determined period of time at a specified pressure and temperature. In this method, wastes are sterilized or disinfected prior to disposal in a landfill. It is both less costly and carries no documented health impacts. 2.) Autoclaving:Īutoclaving, which is also known simply as steam sterilization, is the most commonly utilized alternative to incineration for regulated medical waste management. While some states and localities actively encourage incineration as the preferred method of treatment, others have enacted moratoriums on incinerators to suspend permitting until further information on the safety of the option is available. On-site incineration provides the advantage of a quick, easy disposal method for hazardous medical waste disposal, but there are emissions concerns.
This is the process of burning of waste in temperatures ranging from 1,800☏ to 2,000☏ (982☌ to 1093☌). The information can be overwhelming and difficult to digest, but hopefully this article will help you familiarize yourself with your options for treatment methods for medical waste. There are numerous available and emerging waste treatment technologies to treat Regulated Medical Waste (RMW) and render it less hazardous, each with its own set of advantages and liabilities. Nothing is more important than this step. Once your business has determined that it generates medical waste, it’s necessary that you focus energy on hazardous medical waste disposal and regulated medical waste management. Regulated Medical Waste Treatment Methods


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
